Introduction to Corporate Veil Doctrine
The corporate veil represents one of the most fundamental concepts in Indian company law, serving as the legal foundation that distinguishes a company from its shareholders and owners. This doctrine establishes that a company operates as a separate legal entity, completely independent of the individuals who own, manage, or control it. Understanding this principle is crucial for entrepreneurs, investors, legal professionals, and anyone involved in corporate governance in India.
The significance of the corporate veil extends beyond mere legal technicality—it forms the backbone of modern business operations, enabling companies to function as independent entities capable of owning property, entering contracts, and conducting business activities in their own right. This separation has profound implications for liability, taxation, and business operations across all sectors of the Indian economy.
Defining the Corporate Veil : Legal Meaning and Scope
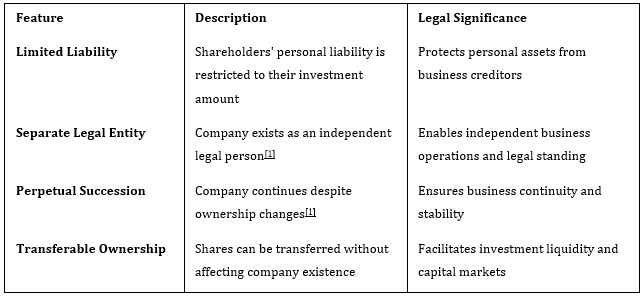
The corporate veil refers to the legal distinction that exists between a company and its shareholders or owners. Under Indian company law, this principle ensures that a company is treated as a separate legal entity with its own distinct identity, rights, and obligations. This separation means that the company can:
· Own property and assets in its own name, independent of its shareholders
· Incur liabilities and debts without directly affecting the personal finances of its owners
· Enter into contracts as an independent legal person
· Sue or be sued in courts as a separate entity
· Continue operations regardless of changes in ownership or management structure
This legal framework is enshrined in the Companies Act, 2013, which serves as the primary legislation governing corporate entities in India. The Act explicitly recognizes companies as independent legal persons, providing them with rights and responsibilities similar to those of natural persons within the legal system.
Primary Purpose and Objectives of the Corporate Veil
The corporate veil doctrine serves several critical purposes in the Indian business landscape:
Protection of Personal Assets
The most significant benefit of the corporate veil is the protection of shareholders’ personal assets. This protection ensures that individual investors are not personally liable for the company’s debts, obligations, or legal issues beyond their initial investment. This limited liability framework creates a safety net that encourages entrepreneurship and investment.
Encouraging Investment and Economic Growth
By limiting personal risk, the corporate veil doctrine encourages investment and risk-taking. Investors are more willing to contribute capital to business ventures when they know their personal wealth remains protected from potential business failures. This protection has been instrumental in driving economic growth and innovation across various industries in India.
Promoting Entrepreneurship
The doctrine creates an environment where entrepreneurs can pursue business opportunities without the fear of unlimited personal liability. This protection enables the pooling of resources and capital from multiple investors, facilitating larger and more ambitious business ventures.
Legal Foundation and Statutory Framework
The corporate veil doctrine is firmly established within the Companies Act,2013, which governs the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies in India. This comprehensive legislation recognizes companies as independent legal persons, distinct from their members, and provides thstatutory framework for corporate operations.
Key provisions of the Act emphasize:
· The company’s legal capacity to own assets and incur liabilities independently
· The separation between company management and ownership
· The principle of perpetual succession, ensuring business continuity
· The transferability of ownership interests without affecting corporate identity
Essential Features of the Corporate Veil
The corporate veil doctrine encompasses several defining characteristics that shape corporate operations in India:
Circumstances for Lifting the Corporate Veil
While the corporate veil provides substantial protection, it is not an absolute shield. Indian courts possess the authority to “lift” or “pierce” the veil in specific circumstances where justice demands intervention. This judicial power ensures that the corporate structure cannot be misused for illegal or fraudulent purposes.
Common Grounds for Veil Lifting
Fraud and Dishonest Conduct: When companies are used as vehicles for fraudulent activities or to evade legal obligations, courts may disregard the separate legal identity and hold individuals personally accountable.
Tax Evasion: The corporate structure cannot be misused to avoid tax obligations. When authorities detect systematic tax evasion through corporate manipulation, the veil may be lifted to reach the actual beneficiaries.
Violation of Statutory Provisions: If companies are used to circumvent laws or public policy, courts may look beyond the corporate structure to ensure legal compliance.
Sham or Agency Companies: When companies serve merely as facades or agents for their owners without genuine independent operations, courts may ignore their separate identity.
Indian Judicial Approach and Precedents
Indian courts have developed a cautious and measured approach to lifting the corporate veil. The judiciary recognizes the importance of maintaining corporate integrity for economic development while ensuring that justice prevails in cases of misuse.
The landmark case of LIC v. Escorts Ltd. established important guidelines for when courts should exercise their power to lift the veil. The Supreme Court emphasized that this power should be used sparingly and only when there is clear evidence of wrong doing or misuse of the corporate structure.
Courts typically require:
· Clear evidence of fraud, illegal activity, or misuse
· Compelling circumstances where justice demands intervention
· Proportionate response that balances corporate protection with legal accountability
Limitations and Judicial Discretion
The power to lift the corporate veil is exercised with considerable restraint. Courts understand that excessive interference with corporate structures could undermine investor confidence and economic growth. Therefore, the doctrine is set aside only in exceptional cases where:
· There exists unambiguous evidence of fraudulent or illegal conduct
· Public interest and justice require looking beyond the corporate structure
· The corporate form is being abused to achieve improper purposes
Conclusion and Future Implications
The doctrine of the corporate veil remains a cornerstone of Indian company law, providing essential protection to shareholders while promoting investment and economic growth. This legal framework has enabled India to develop a robust corporate sector that attracts both domestic and international investment.
However, the doctrine’s effectiveness depends on maintaining the delicate balance between protection and accountability. As business practices evolve and new challenges emerge, the judicial interpretation of when to lift the corporate veil will continue to develop, ensuring that this fundamental principle serves both business interests and the broader public good.
Understanding the nuances of the corporate veil is essential for anyone involved in Indian business or law. By respecting both the protections and limitations of this doctrine, companies and individuals can operate more confidently and responsibly within India’s legal framework, contributing to sustainable economic development and business growth.
